Effective Retrospectives: A Culture of Continuous Improvement
- Niti Deherkar
- /
- December 14, 2023
- /
- Analysis
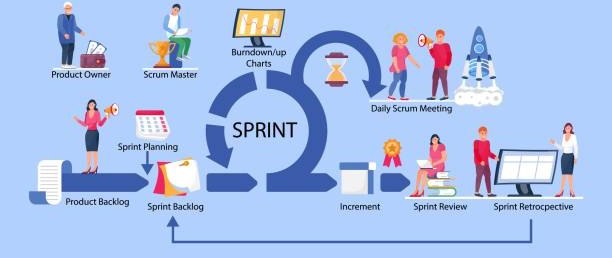
In the fast-paced world of project management, taking time to reflect on past experiences is often overlooked in the rush to move forward. However, effective retrospectives offer a valuable opportunity for teams to pause, reflect, and learn from both successes and failures. In this guide, we'll explore the key elements of effective retrospectives and how they can drive meaningful change and improvement within your team.
Understanding Retrospectives
-
Definition and Purpose: Define retrospectives as structured meetings where teams reflect on their recent experiences, identify areas for improvement, and define actionable steps for change.
-
Importance of Reflection: Emphasize the value of reflection in fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Highlight how retrospectives provide a safe space for open and honest dialogue among team members.
Setting the Stage
-
Creating a Safe Environment: Establish psychological safety within the team to encourage open and honest communication. Emphasize the importance of constructive feedback and mutual respect.
-
Setting Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives for the retrospective meeting. Focus on specific areas of improvement or themes relevant to the team's current challenges and goals.
Facilitation and Participation
-
Effective Facilitation: Assign a neutral facilitator responsible for guiding the retrospective discussion and ensuring all voices are heard. Encourage active participation and engagement from all team members.
-
Structured Approach: Adopt a structured format for the retrospective meeting, such as the "Start, Stop, Continue" or "Mad, Sad, Glad" framework. Provide guiding questions to prompt discussion and reflection.
Analysis and Action
-
Identifying Insights: Encourage team members to share their perspectives on what went well, what could have been improved, and what actions can be taken moving forward. Use techniques like affinity mapping to organize insights.
-
Prioritizing Action Items: Collaboratively prioritize action items based on their impact and feasibility. Focus on defining actionable steps with clear ownership and deadlines.
Continuous Improvement
-
Implementing Change: Follow up on action items from previous retrospectives and track progress towards their implementation. Celebrate successes and address any obstacles or challenges that arise.
-
Iterative Approach: Embrace an iterative approach to retrospectives, holding them regularly (e.g., at the end of each sprint or project phase). Use feedback from previous retrospectives to refine and improve the process over time.
All in All
Effective retrospectives are more than just a box-ticking exercise; they're a powerful tool for driving continuous improvement and fostering team growth. By creating a safe and supportive environment for reflection, facilitating meaningful discussions, and taking actionable steps for change, teams can unlock their full potential and achieve greater success in their projects. Remember, the true value of retrospectives lies not just in looking back but in using those insights to move forward with purpose and clarity.
